What Shareholders Must Know! A Guide to the Exercise Procedures of Shareholders' Right to Know and Judicial Remedies
2025 02/18
In the intricate chess game of the business world,the shareholders'right to know is undoubtedly a trump card in the hands of shareholders.It serves as both a"透视镜"for shareholders to understand the company's operational status and a"legal shield"to safeguard their own rights and interests.
However,in reality,many shareholders find themselves in a predicament due to unclear procedures and a lack of remedies.From the hardships of accessing the company's books to the confusion in judicial litigation,the path to exercising the shareholders'right to know seems to be fraught with thorns.
Through retrieval,the number of cases with the cause of action of"disputes over shareholders'right to know"in recent years is as follows:
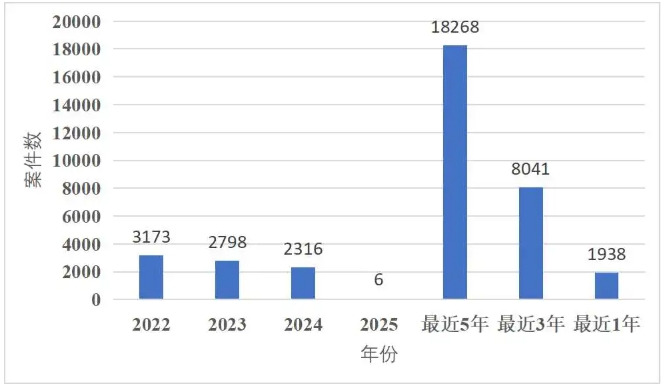
It can be seen that disputes over shareholders'right to know remain frequent cases over the years.
So,how can shareholders exercise their right to know in a standardized manner and effectively seek judicial remedies when they encounter problems in exercising this right?This article will clear the haze for you.From the key points of procedures to judicial remedies,it will comprehensively interpret the legal safeguards for shareholders'right to know,enabling you to have laws to abide by and paths to follow in the game of corporate governance.
I.Regulations Related to Shareholders'Right to Know
The following table comprehensively sorts out the relevant laws and regulations currently related to shareholders'right to know:
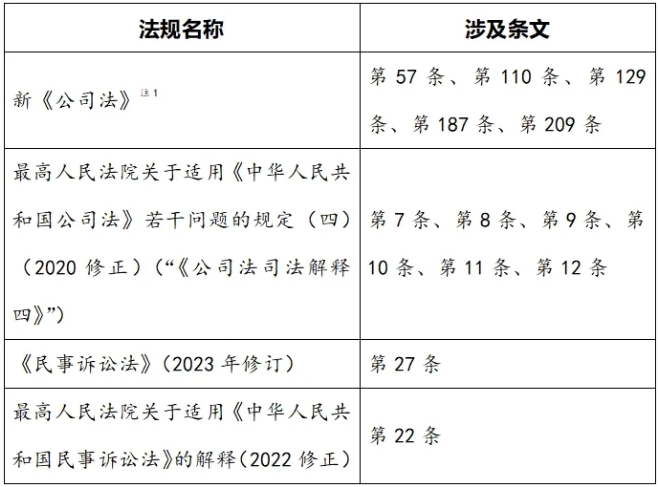
Note 1:
The newly revised"Company Law of the People's Republic of China"(referred to as the"new Company Law")effective on July 1,2024,also has two highlights of revision in the field of shareholders'right to know.Firstly,it expands the scope of the exercise of shareholders'right to know,clearly adding"accounting vouchers"to the shareholders'right to inspect.Secondly,it perfects the way of exercising shareholders'right to know.
II.Scope of Shareholders'Right to Know
Combined with relevant laws and regulations,the scope of shareholders'right to know is visually sorted out as follows:
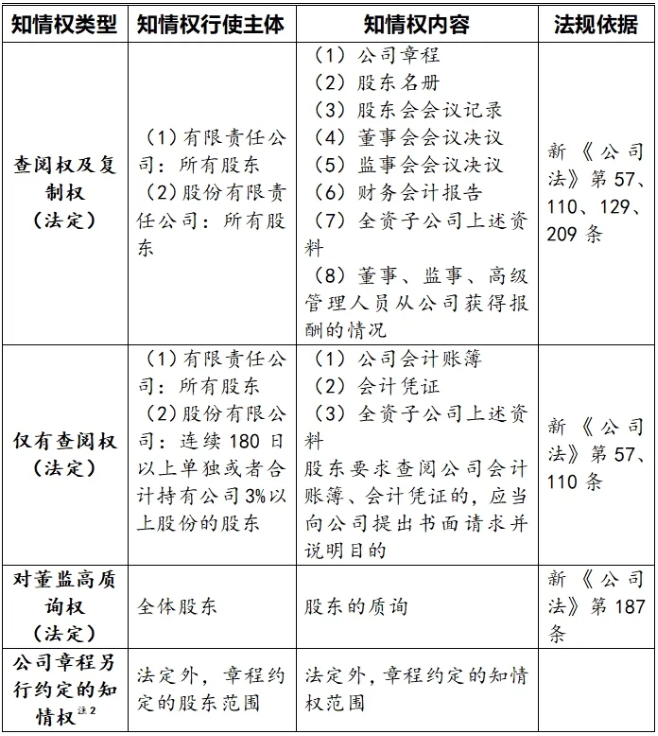
Note 2:
To a certain extent,shareholders'right to know can be otherwise agreed upon through the company's articles of association,but it cannot deviate completely from the Company Law.The specific analysis is as follows:
1.Statutory rights cannot be excluded,and restrictive agreements are generally invalid
Article 9 of the"Judicial Interpretation IV of the Company Law"stipulates that if the company's articles of association,agreements among shareholders,etc.substantially deprive shareholders of the right to inspect or copy the company's documents and materials as stipulated in Article 33 and Article 97 of the Company Law(corresponding to Article 57 and Article 110 of the new Company Law),and the company refuses shareholders'inspection or copying on this ground,the people's court shall not support it.
Shareholders'right to know is a statutory right.The company's articles of association and the majority vote of the shareholders'meeting have no right to exclude shareholders'right to know.When the shareholders'right to know granted by the company's articles of association is smaller than the scope of shareholders'right to know set by the Company Law,the relevant provisions in the articles of association are invalid.
The civil judgment of the Beijing No.1 Intermediate People's Court in(2018)Jing 01 Min Zhong No.2778 states that shareholders'right to know is an inherent right enjoyed by company shareholders based on their capital contributions and shareholder status,and it is the basis for shareholders to participate in company decision-making,operation management,and profit distribution.Except for the restrictive conditions stipulated in the Company Law,it should not be deprived in any form or restricted by the majority vote.The articles of association of Agreya Company stipulate that shareholders need to convene an extraordinary shareholders'meeting to exercise their right to know and obtain the consent of shareholders holding more than two-thirds of the voting rights.This restricts the right to know of minority shareholders in the form of the majority vote of capital,which will lead to minority shareholders being unable to exercise their right to know and unable to understand the company's operation and management situation.The first-instance court determined that the above provisions in the company's articles of association substantially deprived shareholders of their right to know and did not support Agreya Company's claim,which was not improper.In addition,Jin Zhiguo and Agreya Company also stated that Mr.Jin did not agree to and sign the company's articles of association dated March 29,2015.Depriving Mr.Jin of his right to know just because other shareholders agreed to restrict the shareholders'right to know constitutes an abuse of the majority vote of capital and also violates the basic principles of the Company Law.
2.Reasonable expansion is usually effective
The company's articles of association can reasonably expand the scope of shareholders'statutory right to know on the basis of the Company Law.For example,it can be stipulated that shareholders can inspect other company materials in addition to accounting materials and conduct audits of the company and its subsidiaries,etc.,but it is necessary to comprehensively consider the legislative purpose of the Company Law and the individual situation of the company.
III.Exercise of Shareholders'Right to Know
(1)Preparatory Procedures for the Exercise of Shareholders'Right to Know
Article 57 of the new Company Law stipulates that"...Shareholders may request to inspect the company's accounting books and accounting vouchers.When shareholders request to inspect the company's accounting books and accounting vouchers,they shall submit a written request to the company and state the purpose.If the company has reasonable grounds to believe that the shareholders'inspection of accounting books and accounting vouchers has improper purposes and may damage the company's legitimate interests,it may refuse to provide the inspection and shall reply to the shareholders in writing and state the reasons within 15 days as of the date when the shareholders submit the written request.If the company refuses to provide the inspection,the shareholders may file a lawsuit with the people's court.When shareholders inspect the materials specified in the preceding paragraph,they may entrust intermediary institutions such as accounting firms and law firms to conduct the inspection.Shareholders and the intermediary institutions they entrust,such as accounting firms and law firms,shall abide by the relevant laws and administrative regulations on protecting state secrets,trade secrets,personal privacy,and personal information when inspecting and copying relevant materials."
The new Company Law only clearly stipulates the preparatory procedures for shareholders to inspect accounting books and accounting vouchers,but does not stipulate the preparatory procedures for shareholders to inspect and copy the company's articles of association,the shareholder register,the minutes of shareholders'meetings,and other materials.
In order to ensure that shareholders can effectively obtain judicial remedies when the company refuses their application to inspect and copy the company's articles of association,the shareholder register,the minutes of shareholders'meetings,and other materials,it is recommended that whether shareholders only exercise the"right to inspect"or exercise the"right to inspect and copy",they should operate in accordance with the preparatory procedures for applying to inspect accounting books and accounting vouchers to ensure the integrity of the shareholders'application process and leave written procedural documents as evidence support for subsequent litigation.
Combined with the regulations and relevant judicial precedents,the general procedures for shareholders to exercise their right to know are as follows:
Step 1:Shareholders submit a written inspection application to the company and state the inspection purpose
Step 2:Shareholders serve the written application on the company
Suggestions:(1)Serve the paper application on the company via EMS postal express and clearly note"Application for the Exercise of Shareholders'Right to Know by Shareholder XXX";(2)Send it synchronously in electronic form to the company's publicly announced or previously provided email addresses,WeChat,or other electronic media(such as Enterprise WeChat,DingTalk,Feishu,etc.)for daily communication and receiving of shareholders'letters and documents,and indicate in the sending that the document is"Application for the Exercise of Shareholders'Right to Know by Shareholder XXX".
Step 3:Wait for the company to review the shareholders'inspection application and see if the company replies in writing within 15 days
Step 4:If the company agrees,it provides convenience for shareholders to exercise their right to know,and shareholders go to exercise their right to know
Step 5:If the company refuses,it must reply to the shareholders in writing and state the reasons for refusal within 15 days as of the date when the shareholders submit the written request
Step 6:In the case of the company's refusal,shareholders may file a lawsuit with the court
(2)Contents to be Clearly Stated in the Written Application
In order to prevent the exercise of shareholders'right to know from being affected by procedural defects or having an adverse impact on future rights protection through judicial channels,it is recommended that the written application submitted by shareholders to the company must clearly state the following contents:
1.Specify the specific names and time ranges of the documents to be inspected or copied
For example,state:(1)Apply to inspect all the minutes of shareholders'meetings and resolutions of the board of directors of XX Company from January 1,2020,to December 31,2020(inclusive),and provide the original paper version for inspection and copying;(2)Apply to inspect the accounting books(including general ledgers,subsidiary ledgers,journals,and other subsidiary books)and accounting vouchers(including original vouchers and accounting vouchers)formed during the period from January 1,2020,to December 31,2020(inclusive).
2.Specify the inspection method and inspection personnel
Whether to entrust an intermediary institution(law firm or accounting firm)to inspect or copy,for example:Our company entrusts one lawyer to go for inspection and copying.
3.Specify the inspection time and place
The purpose of the Company Law in endowing shareholders with the right to know is to ensure the full exercise of shareholders'rights.The exercise of this right should be carried out under a mechanism of rights balance,that is,it should not have an adverse impact on the company's rights and interests such as business efficiency and business order.
According to the existing relevant court precedents,it is usually required that the inspection and copying should be carried out during the company's normal business hours and should not exceed 15 working days(see(2022)Jing 02 Min Zhong No.2522 for details).
For example,state:Our inspection personnel will conduct inspection or copying at the actual business location XXX of the company from 9:00 on February 1,2025,to 18:00 on February 1,2025.Please provide a meeting room for our personnel to inspect and copy at that time.
4.Specify the inspection purpose
For example,state:Only to understand the company's financial situation or business situation,etc.
Note:The four situations in Article 8 of the"Judicial Interpretation IV of the Company Law"are regarded as having"improper purposes",but the burden of proof lies with the company.
5.Other contents to be stated
For example,state:The specific tools that the inspection personnel will carry for copying or inspection,or the need for the company to provide copying convenience,etc.
(3)Inspection and Copying Personnel
1.Scope of Personnel
According to the third and fourth paragraphs of Article 57 of the new Company Law,when shareholders inspect the materials specified in the preceding paragraph,they may entrust intermediary institutions such as accounting firms and law firms to conduct the inspection.Shareholders and the intermediary institutions they entrust,such as accounting firms and law firms,shall abide by the relevant laws and administrative regulations on protecting state secrets,trade secrets,personal privacy,and personal information when inspecting and copying relevant materials.
According to the above provisions,the specific scope of personnel for shareholders to exercise their right to know is as follows:
(1)Shareholders themselves:If the shareholder is a natural person,he/she shall go with his/her ID;if the shareholder is a legal person or other organization,its legal representative,operator,executive partner(or its appointed representative),etc.shall go with their IDs;
(2)Professional personnel of intermediary institutions entrusted by shareholders:Lawyers of law firms,accountants of accounting firms,etc.shall go with the power of attorney,introduction letter,and ID,and it is no longer required that the shareholder must be present;
(3)Internal employees entrusted by shareholders:If the shareholder is a legal person or other organization,it may entrust its employees to exercise the right to know on its behalf,and the employees shall go with the power of attorney and ID;
(4)Note:According to the second paragraph of Article 10 of the"Judicial Interpretation IV of the Company Law",when shareholders inspect the company's documents and materials according to the effective judgment of the people's court,in the presence of the shareholder,practicing personnel of intermediary institutions such as accountants and lawyers who are legally or according to the professional conduct norms obliged to keep secrets may assist in the inspection.That is,when the shareholders'right to know is supported by the court's judgment,the shareholder must be present at this time,and accountants,lawyers,etc.are only assisting personnel.
2.Whether There Is a Limit on the Number of Personnel
The law does not limit the number of personnel going for inspection and copying.However,it is still on the premise of not having an adverse impact on the company's business efficiency,business order,and other rights and interests.Shareholders should reasonably determine the number of personnel going for inspection and copying according to their personal situations and prior communication with the company.
(4)Whether Excerpting Is Allowed for Accounting Books and Accounting Voucher Materials Only for Inspection
The law does not clearly state whether"inspection"includes the act of"excerpting".However,after reviewing relevant precedents,the author tends to believe that"inspection"includes the act of"excerpting".The following is a precedent of the Haidian Court that was reversed by the Beijing No.1 Intermediate People's Court.The explanation made by the No.1 Intermediate People's Court is,in the author's opinion,quite persuasive and more in line with the original intention of the shareholders'right to know granted by the Company Law:
The Executive Behavior Objection and Executive Reconsideration Ruling of Beijing XX Investment Management Co.,Ltd.and XX Communication Group Co.,Ltd.[Trial Court:Beijing No.1 Intermediate People's Court,Case No.:(2021)Jing 01 Zhi Fu No.195]
This court believes that the focus of the dispute in this case is as follows:First,whether XX Investment Management Company can excerpt when exercising its shareholders'right to know and inspect the accounting books and accounting vouchers.
Regarding the issue of whether XX Investment Management Company can excerpt when exercising its shareholders'right to know and inspect the accounting books and accounting vouchers of XX Communication Company.From the understanding of the word meaning,duplication refers to the act of making one or more copies of the original in the forms of printing,photocopying,tracing,rubbing,video recording,photo copying,etc.,while excerpting can be understood as extracting some contents or information from books or documents for copying.It can be seen that duplication can produce an effect the same as or similar to the appearance of the original.However,generally speaking,excerpting can only present part of the contents of the original and cannot reflect the overall picture and general situation of the original,and it does not produce an effect the same as or similar to the appearance of the original.Therefore,excerpting is usually not the same as duplication.In addition,shareholders'right to know is the right of company shareholders to understand the company's information and be aware of the company's affairs.The time span of the accounting books and accounting vouchers that XX Communication Company should provide for XX Investment Management Company to inspect as determined by the enforcement basis in this case is from February 24,2006,to the effective date of the enforcement basis,spanning more than ten years.Moreover,the accounting books and accounting vouchers contain a large amount of professional data information.It is difficult to ensure that XX Investment Management Company can fully understand and be aware of the financial situation and business situation of XX Communication Company just by reading and memorizing,which will make the exercise of shareholders'right to know a mere formality.When excerpting does not produce an effect similar or identical to the appearance of the original and there is no evidence to prove that XX Investment Management Company's exercise of shareholders'right to know will disclose the trade secrets or information of XX Communication Company,resulting in damage to the company's legitimate interests,excerpting should be regarded as a means to assist shareholders in exercising their right to know and inspect the accounting books and accounting vouchers.Moreover,inspection itself means checking and observing,not just viewing and reading.Excerpting is one of the ways of checking.Combining with the circumstances of this case,inspection can be extended to excerpting.Therefore,when XX Communication Company performs the obligations of the above judgment items,it should provide a venue and conditions that meet the requirements to ensure the legitimate exercise of XX Investment Management Company's shareholders'right to know.
The author highly agrees with the above explanation of the No.1 Intermediate People's Court.If"inspection"is just by means of"reading and memorizing",it will become a mere formality.Since"excerpting"does not produce an effect the same as or similar to the appearance of the original,it is not equal to"duplication".Combining with the specific case situation,for a large number of complex materials,"excerpting"should be regarded as one of the means to assist shareholders in exercising the"inspection"right to know.
IV.Judicial Remedies When Shareholders'Exercise of the Right to Know Is Hindered
Both the new Company Law and the"Judicial Interpretation IV of the Company Law"stipulate that when the company refuses to cooperate to ensure that shareholders exercise their right to know,shareholders can file a lawsuit with the people's court.Then,before filing a lawsuit,in addition to fully preparing the above preparatory procedures,some issues regarding judicial remedies(such as the jurisdiction court,the cause of action,the claims in the lawsuit,etc.)are sorted out as follows:
(1)Jurisdiction Court
Article 22 of the"Interpretation of the Supreme People's Court on the Application of the Civil Procedure Law of the People's Republic of China"(Amended in 2022)stipulates that for lawsuits filed due to disputes such as the recording of the shareholder register,requests for changing company registration,shareholders'right to know,company resolutions,company mergers,company divisions,company capital reduction,and company capital increase,the jurisdiction shall be determined in accordance with Article 27 of the Civil Procedure Law.
Article 27 of the Civil Procedure Law stipulates that for lawsuits filed due to disputes such as company establishment,confirmation of shareholder qualifications,profit distribution,and company dissolution,they shall be under the jurisdiction of the people's court in the place where the company is domiciled.
According to the above provisions,disputes between shareholders whose exercise of the right to know is obstructed and the company fall within the circumstances stipulated in Article 27 of the Civil Procedure Law,and shall be under the jurisdiction of the people's court in the place where the company is domiciled.
(2)Cause of Action and Litigation Parties
1.Cause of Action for Civil Cases
There is a specific name for the cause of action regarding disputes over shareholders'right to know.
In the"Provisions on the Cause of Action for Civil Cases"(Revised in 2020),under"Part VIII:Civil Disputes Related to Companies,Securities,Insurance,Negotiable Instruments,etc.",in"21.Disputes Related to Companies",there is"267.Disputes over Shareholders'Right to Know".
"Disputes over Shareholders'Right to Know"exists as a third-level cause of action under disputes related to companies.Therefore,the selection and application of the cause of action are relatively clear.
2.Litigation Parties
Plaintiff:Shareholders whose exercise of the right to know is obstructed
Defendant:The company where the shareholders are located
(3)Claims in the Lawsuit
Regarding disputes over shareholders'right to know,several adjudicated precedents that the author deems comprehensive and standardized have been found for reference:
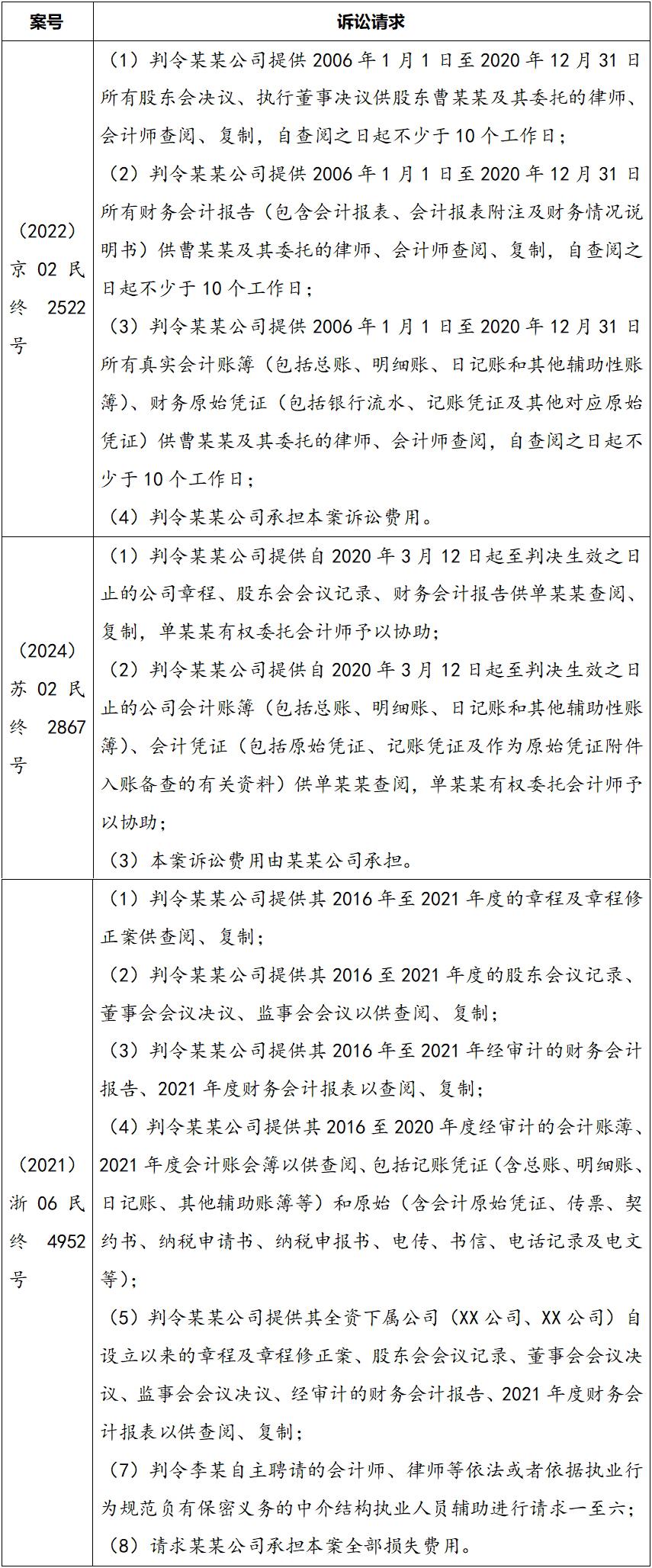
Based on the above precedents and combined with the final judgment results of the court,the following points should be noted when listing the claims:
(1)Clearly specify the specific types,names,and time ranges of the documents to be inspected and copied;
(2)Clearly define the specific right to be exercised,whether it is the"right to inspect"or the"right to inspect and copy";
(3)Clearly state the permitted time,personnel,location,etc.for the inspection;
(4)Other obligations or responsibilities that the company should bear and need to be specified.
V.Conclusion
Shareholders'right to know is an important cornerstone for shareholders to participate in corporate governance and safeguard their own rights and interests.
In actual operation,shareholders should attach importance to every detail.From clarifying the regulations and defining the scope,to exercising rights in accordance with the regulations,and then to seeking judicial remedies when obstructed,every step should not be ignored.At the same time,whether it is the standardization of the procedures for inspecting documents or the grasp of the timing of litigation for rights protection,shareholders need to treat them with caution.
In a complex business environment,only by accurately grasping these key points can shareholders better safeguard their own rights and interests and ensure their investment returns.
However,in reality,many shareholders find themselves in a predicament due to unclear procedures and a lack of remedies.From the hardships of accessing the company's books to the confusion in judicial litigation,the path to exercising the shareholders'right to know seems to be fraught with thorns.
Through retrieval,the number of cases with the cause of action of"disputes over shareholders'right to know"in recent years is as follows:

Source:Wolters Kluwer;Inquiry Date:February 14,2025
It can be seen that disputes over shareholders'right to know remain frequent cases over the years.
So,how can shareholders exercise their right to know in a standardized manner and effectively seek judicial remedies when they encounter problems in exercising this right?This article will clear the haze for you.From the key points of procedures to judicial remedies,it will comprehensively interpret the legal safeguards for shareholders'right to know,enabling you to have laws to abide by and paths to follow in the game of corporate governance.
I.Regulations Related to Shareholders'Right to Know
The following table comprehensively sorts out the relevant laws and regulations currently related to shareholders'right to know:

Note 1:
The newly revised"Company Law of the People's Republic of China"(referred to as the"new Company Law")effective on July 1,2024,also has two highlights of revision in the field of shareholders'right to know.Firstly,it expands the scope of the exercise of shareholders'right to know,clearly adding"accounting vouchers"to the shareholders'right to inspect.Secondly,it perfects the way of exercising shareholders'right to know.
II.Scope of Shareholders'Right to Know
Combined with relevant laws and regulations,the scope of shareholders'right to know is visually sorted out as follows:

Note 2:
To a certain extent,shareholders'right to know can be otherwise agreed upon through the company's articles of association,but it cannot deviate completely from the Company Law.The specific analysis is as follows:
1.Statutory rights cannot be excluded,and restrictive agreements are generally invalid
Article 9 of the"Judicial Interpretation IV of the Company Law"stipulates that if the company's articles of association,agreements among shareholders,etc.substantially deprive shareholders of the right to inspect or copy the company's documents and materials as stipulated in Article 33 and Article 97 of the Company Law(corresponding to Article 57 and Article 110 of the new Company Law),and the company refuses shareholders'inspection or copying on this ground,the people's court shall not support it.
Shareholders'right to know is a statutory right.The company's articles of association and the majority vote of the shareholders'meeting have no right to exclude shareholders'right to know.When the shareholders'right to know granted by the company's articles of association is smaller than the scope of shareholders'right to know set by the Company Law,the relevant provisions in the articles of association are invalid.
The civil judgment of the Beijing No.1 Intermediate People's Court in(2018)Jing 01 Min Zhong No.2778 states that shareholders'right to know is an inherent right enjoyed by company shareholders based on their capital contributions and shareholder status,and it is the basis for shareholders to participate in company decision-making,operation management,and profit distribution.Except for the restrictive conditions stipulated in the Company Law,it should not be deprived in any form or restricted by the majority vote.The articles of association of Agreya Company stipulate that shareholders need to convene an extraordinary shareholders'meeting to exercise their right to know and obtain the consent of shareholders holding more than two-thirds of the voting rights.This restricts the right to know of minority shareholders in the form of the majority vote of capital,which will lead to minority shareholders being unable to exercise their right to know and unable to understand the company's operation and management situation.The first-instance court determined that the above provisions in the company's articles of association substantially deprived shareholders of their right to know and did not support Agreya Company's claim,which was not improper.In addition,Jin Zhiguo and Agreya Company also stated that Mr.Jin did not agree to and sign the company's articles of association dated March 29,2015.Depriving Mr.Jin of his right to know just because other shareholders agreed to restrict the shareholders'right to know constitutes an abuse of the majority vote of capital and also violates the basic principles of the Company Law.
2.Reasonable expansion is usually effective
The company's articles of association can reasonably expand the scope of shareholders'statutory right to know on the basis of the Company Law.For example,it can be stipulated that shareholders can inspect other company materials in addition to accounting materials and conduct audits of the company and its subsidiaries,etc.,but it is necessary to comprehensively consider the legislative purpose of the Company Law and the individual situation of the company.
III.Exercise of Shareholders'Right to Know
(1)Preparatory Procedures for the Exercise of Shareholders'Right to Know
Article 57 of the new Company Law stipulates that"...Shareholders may request to inspect the company's accounting books and accounting vouchers.When shareholders request to inspect the company's accounting books and accounting vouchers,they shall submit a written request to the company and state the purpose.If the company has reasonable grounds to believe that the shareholders'inspection of accounting books and accounting vouchers has improper purposes and may damage the company's legitimate interests,it may refuse to provide the inspection and shall reply to the shareholders in writing and state the reasons within 15 days as of the date when the shareholders submit the written request.If the company refuses to provide the inspection,the shareholders may file a lawsuit with the people's court.When shareholders inspect the materials specified in the preceding paragraph,they may entrust intermediary institutions such as accounting firms and law firms to conduct the inspection.Shareholders and the intermediary institutions they entrust,such as accounting firms and law firms,shall abide by the relevant laws and administrative regulations on protecting state secrets,trade secrets,personal privacy,and personal information when inspecting and copying relevant materials."
The new Company Law only clearly stipulates the preparatory procedures for shareholders to inspect accounting books and accounting vouchers,but does not stipulate the preparatory procedures for shareholders to inspect and copy the company's articles of association,the shareholder register,the minutes of shareholders'meetings,and other materials.
In order to ensure that shareholders can effectively obtain judicial remedies when the company refuses their application to inspect and copy the company's articles of association,the shareholder register,the minutes of shareholders'meetings,and other materials,it is recommended that whether shareholders only exercise the"right to inspect"or exercise the"right to inspect and copy",they should operate in accordance with the preparatory procedures for applying to inspect accounting books and accounting vouchers to ensure the integrity of the shareholders'application process and leave written procedural documents as evidence support for subsequent litigation.
Combined with the regulations and relevant judicial precedents,the general procedures for shareholders to exercise their right to know are as follows:
Step 1:Shareholders submit a written inspection application to the company and state the inspection purpose
Step 2:Shareholders serve the written application on the company
Suggestions:(1)Serve the paper application on the company via EMS postal express and clearly note"Application for the Exercise of Shareholders'Right to Know by Shareholder XXX";(2)Send it synchronously in electronic form to the company's publicly announced or previously provided email addresses,WeChat,or other electronic media(such as Enterprise WeChat,DingTalk,Feishu,etc.)for daily communication and receiving of shareholders'letters and documents,and indicate in the sending that the document is"Application for the Exercise of Shareholders'Right to Know by Shareholder XXX".
Step 3:Wait for the company to review the shareholders'inspection application and see if the company replies in writing within 15 days
Step 4:If the company agrees,it provides convenience for shareholders to exercise their right to know,and shareholders go to exercise their right to know
Step 5:If the company refuses,it must reply to the shareholders in writing and state the reasons for refusal within 15 days as of the date when the shareholders submit the written request
Step 6:In the case of the company's refusal,shareholders may file a lawsuit with the court
(2)Contents to be Clearly Stated in the Written Application
In order to prevent the exercise of shareholders'right to know from being affected by procedural defects or having an adverse impact on future rights protection through judicial channels,it is recommended that the written application submitted by shareholders to the company must clearly state the following contents:
1.Specify the specific names and time ranges of the documents to be inspected or copied
For example,state:(1)Apply to inspect all the minutes of shareholders'meetings and resolutions of the board of directors of XX Company from January 1,2020,to December 31,2020(inclusive),and provide the original paper version for inspection and copying;(2)Apply to inspect the accounting books(including general ledgers,subsidiary ledgers,journals,and other subsidiary books)and accounting vouchers(including original vouchers and accounting vouchers)formed during the period from January 1,2020,to December 31,2020(inclusive).
2.Specify the inspection method and inspection personnel
Whether to entrust an intermediary institution(law firm or accounting firm)to inspect or copy,for example:Our company entrusts one lawyer to go for inspection and copying.
3.Specify the inspection time and place
The purpose of the Company Law in endowing shareholders with the right to know is to ensure the full exercise of shareholders'rights.The exercise of this right should be carried out under a mechanism of rights balance,that is,it should not have an adverse impact on the company's rights and interests such as business efficiency and business order.
According to the existing relevant court precedents,it is usually required that the inspection and copying should be carried out during the company's normal business hours and should not exceed 15 working days(see(2022)Jing 02 Min Zhong No.2522 for details).
For example,state:Our inspection personnel will conduct inspection or copying at the actual business location XXX of the company from 9:00 on February 1,2025,to 18:00 on February 1,2025.Please provide a meeting room for our personnel to inspect and copy at that time.
4.Specify the inspection purpose
For example,state:Only to understand the company's financial situation or business situation,etc.
Note:The four situations in Article 8 of the"Judicial Interpretation IV of the Company Law"are regarded as having"improper purposes",but the burden of proof lies with the company.
5.Other contents to be stated
For example,state:The specific tools that the inspection personnel will carry for copying or inspection,or the need for the company to provide copying convenience,etc.
(3)Inspection and Copying Personnel
1.Scope of Personnel
According to the third and fourth paragraphs of Article 57 of the new Company Law,when shareholders inspect the materials specified in the preceding paragraph,they may entrust intermediary institutions such as accounting firms and law firms to conduct the inspection.Shareholders and the intermediary institutions they entrust,such as accounting firms and law firms,shall abide by the relevant laws and administrative regulations on protecting state secrets,trade secrets,personal privacy,and personal information when inspecting and copying relevant materials.
According to the above provisions,the specific scope of personnel for shareholders to exercise their right to know is as follows:
(1)Shareholders themselves:If the shareholder is a natural person,he/she shall go with his/her ID;if the shareholder is a legal person or other organization,its legal representative,operator,executive partner(or its appointed representative),etc.shall go with their IDs;
(2)Professional personnel of intermediary institutions entrusted by shareholders:Lawyers of law firms,accountants of accounting firms,etc.shall go with the power of attorney,introduction letter,and ID,and it is no longer required that the shareholder must be present;
(3)Internal employees entrusted by shareholders:If the shareholder is a legal person or other organization,it may entrust its employees to exercise the right to know on its behalf,and the employees shall go with the power of attorney and ID;
(4)Note:According to the second paragraph of Article 10 of the"Judicial Interpretation IV of the Company Law",when shareholders inspect the company's documents and materials according to the effective judgment of the people's court,in the presence of the shareholder,practicing personnel of intermediary institutions such as accountants and lawyers who are legally or according to the professional conduct norms obliged to keep secrets may assist in the inspection.That is,when the shareholders'right to know is supported by the court's judgment,the shareholder must be present at this time,and accountants,lawyers,etc.are only assisting personnel.
2.Whether There Is a Limit on the Number of Personnel
The law does not limit the number of personnel going for inspection and copying.However,it is still on the premise of not having an adverse impact on the company's business efficiency,business order,and other rights and interests.Shareholders should reasonably determine the number of personnel going for inspection and copying according to their personal situations and prior communication with the company.
(4)Whether Excerpting Is Allowed for Accounting Books and Accounting Voucher Materials Only for Inspection
The law does not clearly state whether"inspection"includes the act of"excerpting".However,after reviewing relevant precedents,the author tends to believe that"inspection"includes the act of"excerpting".The following is a precedent of the Haidian Court that was reversed by the Beijing No.1 Intermediate People's Court.The explanation made by the No.1 Intermediate People's Court is,in the author's opinion,quite persuasive and more in line with the original intention of the shareholders'right to know granted by the Company Law:
The Executive Behavior Objection and Executive Reconsideration Ruling of Beijing XX Investment Management Co.,Ltd.and XX Communication Group Co.,Ltd.[Trial Court:Beijing No.1 Intermediate People's Court,Case No.:(2021)Jing 01 Zhi Fu No.195]
This court believes that the focus of the dispute in this case is as follows:First,whether XX Investment Management Company can excerpt when exercising its shareholders'right to know and inspect the accounting books and accounting vouchers.
Regarding the issue of whether XX Investment Management Company can excerpt when exercising its shareholders'right to know and inspect the accounting books and accounting vouchers of XX Communication Company.From the understanding of the word meaning,duplication refers to the act of making one or more copies of the original in the forms of printing,photocopying,tracing,rubbing,video recording,photo copying,etc.,while excerpting can be understood as extracting some contents or information from books or documents for copying.It can be seen that duplication can produce an effect the same as or similar to the appearance of the original.However,generally speaking,excerpting can only present part of the contents of the original and cannot reflect the overall picture and general situation of the original,and it does not produce an effect the same as or similar to the appearance of the original.Therefore,excerpting is usually not the same as duplication.In addition,shareholders'right to know is the right of company shareholders to understand the company's information and be aware of the company's affairs.The time span of the accounting books and accounting vouchers that XX Communication Company should provide for XX Investment Management Company to inspect as determined by the enforcement basis in this case is from February 24,2006,to the effective date of the enforcement basis,spanning more than ten years.Moreover,the accounting books and accounting vouchers contain a large amount of professional data information.It is difficult to ensure that XX Investment Management Company can fully understand and be aware of the financial situation and business situation of XX Communication Company just by reading and memorizing,which will make the exercise of shareholders'right to know a mere formality.When excerpting does not produce an effect similar or identical to the appearance of the original and there is no evidence to prove that XX Investment Management Company's exercise of shareholders'right to know will disclose the trade secrets or information of XX Communication Company,resulting in damage to the company's legitimate interests,excerpting should be regarded as a means to assist shareholders in exercising their right to know and inspect the accounting books and accounting vouchers.Moreover,inspection itself means checking and observing,not just viewing and reading.Excerpting is one of the ways of checking.Combining with the circumstances of this case,inspection can be extended to excerpting.Therefore,when XX Communication Company performs the obligations of the above judgment items,it should provide a venue and conditions that meet the requirements to ensure the legitimate exercise of XX Investment Management Company's shareholders'right to know.
The author highly agrees with the above explanation of the No.1 Intermediate People's Court.If"inspection"is just by means of"reading and memorizing",it will become a mere formality.Since"excerpting"does not produce an effect the same as or similar to the appearance of the original,it is not equal to"duplication".Combining with the specific case situation,for a large number of complex materials,"excerpting"should be regarded as one of the means to assist shareholders in exercising the"inspection"right to know.
IV.Judicial Remedies When Shareholders'Exercise of the Right to Know Is Hindered
Both the new Company Law and the"Judicial Interpretation IV of the Company Law"stipulate that when the company refuses to cooperate to ensure that shareholders exercise their right to know,shareholders can file a lawsuit with the people's court.Then,before filing a lawsuit,in addition to fully preparing the above preparatory procedures,some issues regarding judicial remedies(such as the jurisdiction court,the cause of action,the claims in the lawsuit,etc.)are sorted out as follows:
(1)Jurisdiction Court
Article 22 of the"Interpretation of the Supreme People's Court on the Application of the Civil Procedure Law of the People's Republic of China"(Amended in 2022)stipulates that for lawsuits filed due to disputes such as the recording of the shareholder register,requests for changing company registration,shareholders'right to know,company resolutions,company mergers,company divisions,company capital reduction,and company capital increase,the jurisdiction shall be determined in accordance with Article 27 of the Civil Procedure Law.
Article 27 of the Civil Procedure Law stipulates that for lawsuits filed due to disputes such as company establishment,confirmation of shareholder qualifications,profit distribution,and company dissolution,they shall be under the jurisdiction of the people's court in the place where the company is domiciled.
According to the above provisions,disputes between shareholders whose exercise of the right to know is obstructed and the company fall within the circumstances stipulated in Article 27 of the Civil Procedure Law,and shall be under the jurisdiction of the people's court in the place where the company is domiciled.
(2)Cause of Action and Litigation Parties
1.Cause of Action for Civil Cases
There is a specific name for the cause of action regarding disputes over shareholders'right to know.
In the"Provisions on the Cause of Action for Civil Cases"(Revised in 2020),under"Part VIII:Civil Disputes Related to Companies,Securities,Insurance,Negotiable Instruments,etc.",in"21.Disputes Related to Companies",there is"267.Disputes over Shareholders'Right to Know".
"Disputes over Shareholders'Right to Know"exists as a third-level cause of action under disputes related to companies.Therefore,the selection and application of the cause of action are relatively clear.
2.Litigation Parties
Plaintiff:Shareholders whose exercise of the right to know is obstructed
Defendant:The company where the shareholders are located
(3)Claims in the Lawsuit
Regarding disputes over shareholders'right to know,several adjudicated precedents that the author deems comprehensive and standardized have been found for reference:

Based on the above precedents and combined with the final judgment results of the court,the following points should be noted when listing the claims:
(1)Clearly specify the specific types,names,and time ranges of the documents to be inspected and copied;
(2)Clearly define the specific right to be exercised,whether it is the"right to inspect"or the"right to inspect and copy";
(3)Clearly state the permitted time,personnel,location,etc.for the inspection;
(4)Other obligations or responsibilities that the company should bear and need to be specified.
V.Conclusion
Shareholders'right to know is an important cornerstone for shareholders to participate in corporate governance and safeguard their own rights and interests.
In actual operation,shareholders should attach importance to every detail.From clarifying the regulations and defining the scope,to exercising rights in accordance with the regulations,and then to seeking judicial remedies when obstructed,every step should not be ignored.At the same time,whether it is the standardization of the procedures for inspecting documents or the grasp of the timing of litigation for rights protection,shareholders need to treat them with caution.
In a complex business environment,only by accurately grasping these key points can shareholders better safeguard their own rights and interests and ensure their investment returns.